Load cases and load combinations¶
Load cases¶
You can group different loads in a single load case and add these to a SystemElements object. Let’s look at an example. First we create a frame girder.
from anastruct import SystemElements
from anastruct import LoadCase, LoadCombination
import numpy as np
ss = SystemElements()
height = 10
x = np.cumsum([0, 4, 7, 7, 4])
y = np.zeros(x.shape)
x = np.append(x, x[::-1])
y = np.append(y, y + height)
ss.add_element_grid(x, y)
ss.add_element([[0, 0], [0, height]])
ss.add_element([[4, 0], [4, height]])
ss.add_element([[11, 0], [11, height]])
ss.add_element([[18, 0], [18, height]])
ss.add_support_hinged([1, 5])
ss.show_structure()
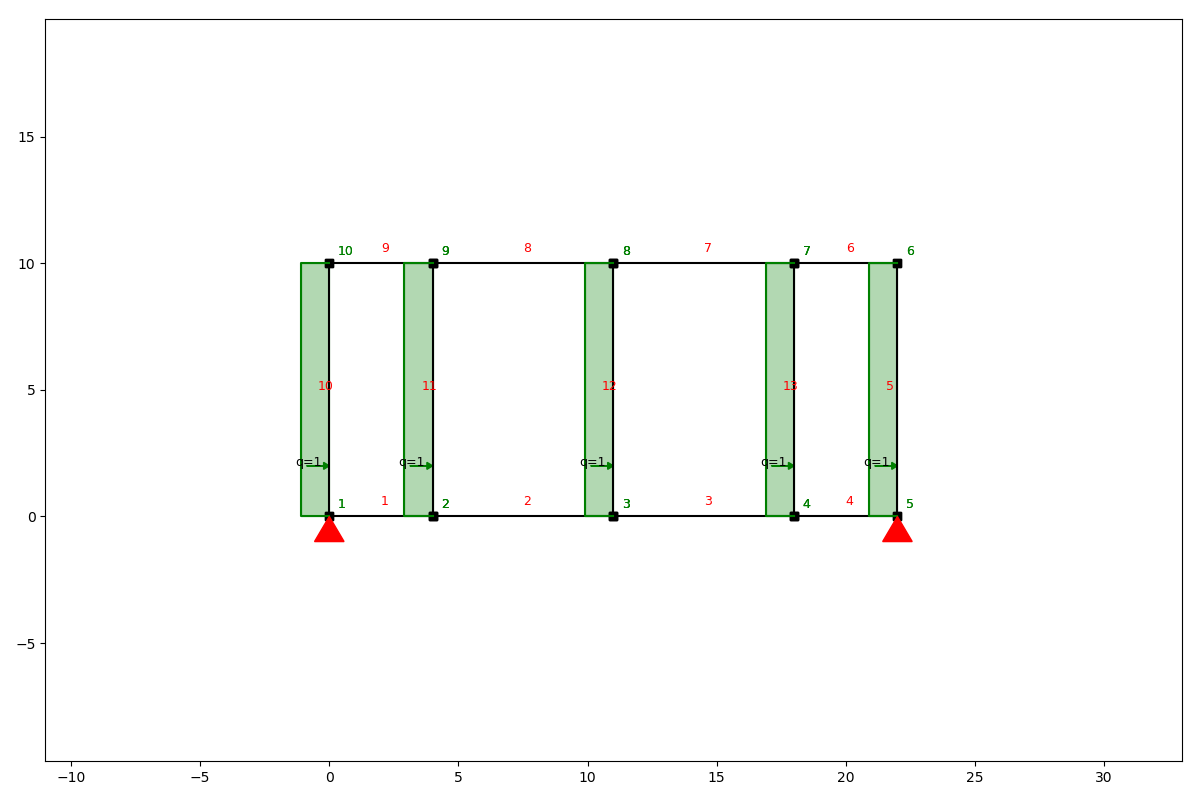
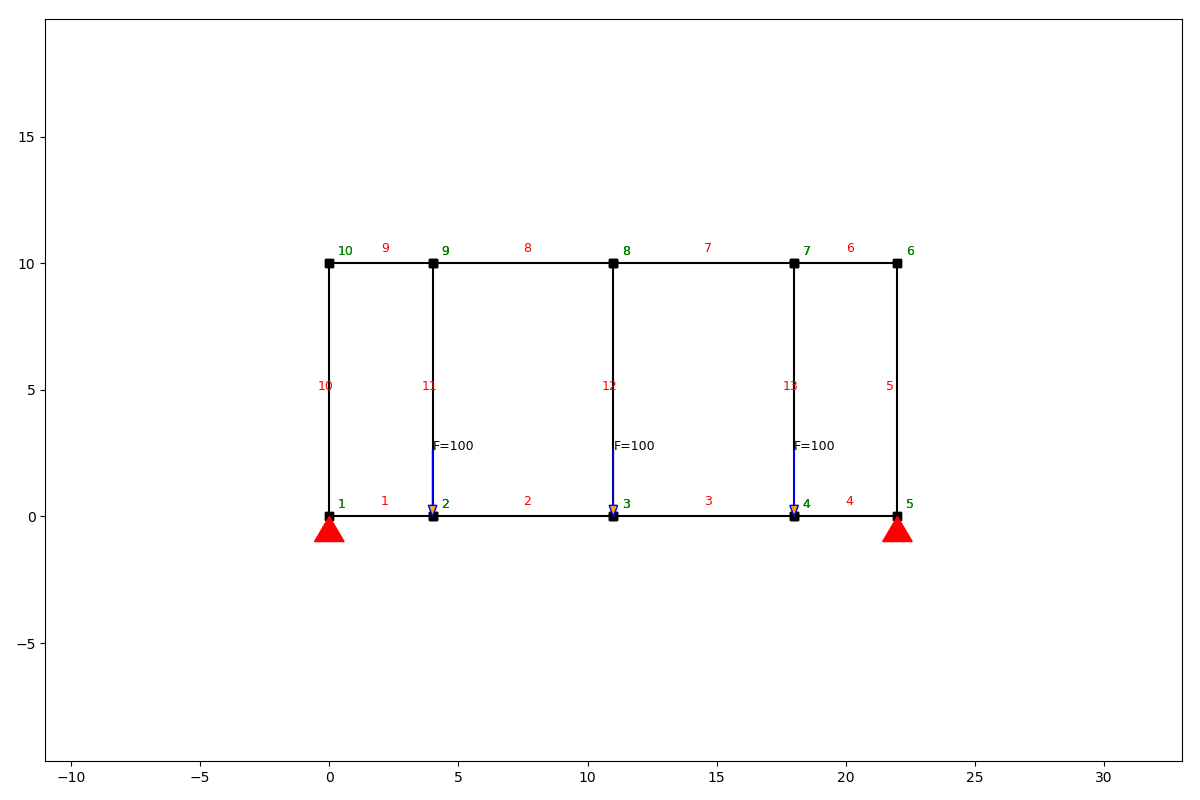
Now we can add a loadcase for all the wind loads.
lc_wind = LoadCase('wind')
lc_wind.q_load(q=-1, element_id=[10, 11, 12, 13, 5])
print(lc_wind)
output
Loadcase wind:
{'q_load-1': {'direction': 'element',
'element_id': [10, 11, 12, 13, 5],
'q': -1}}
And apply to the load case to our system.
# add the load case to the SystemElements object
ss.apply_load_case(lc_wind)
ss.show_structure()
Load combinations¶
We can also combine load cases in a load combination with the LoadCombination class. First remove the previous load case from the system, create a LoadCombination object and add the LoadCase objects to the LoadCombination object.
# reset the structure
ss.remove_loads()
# create another load case
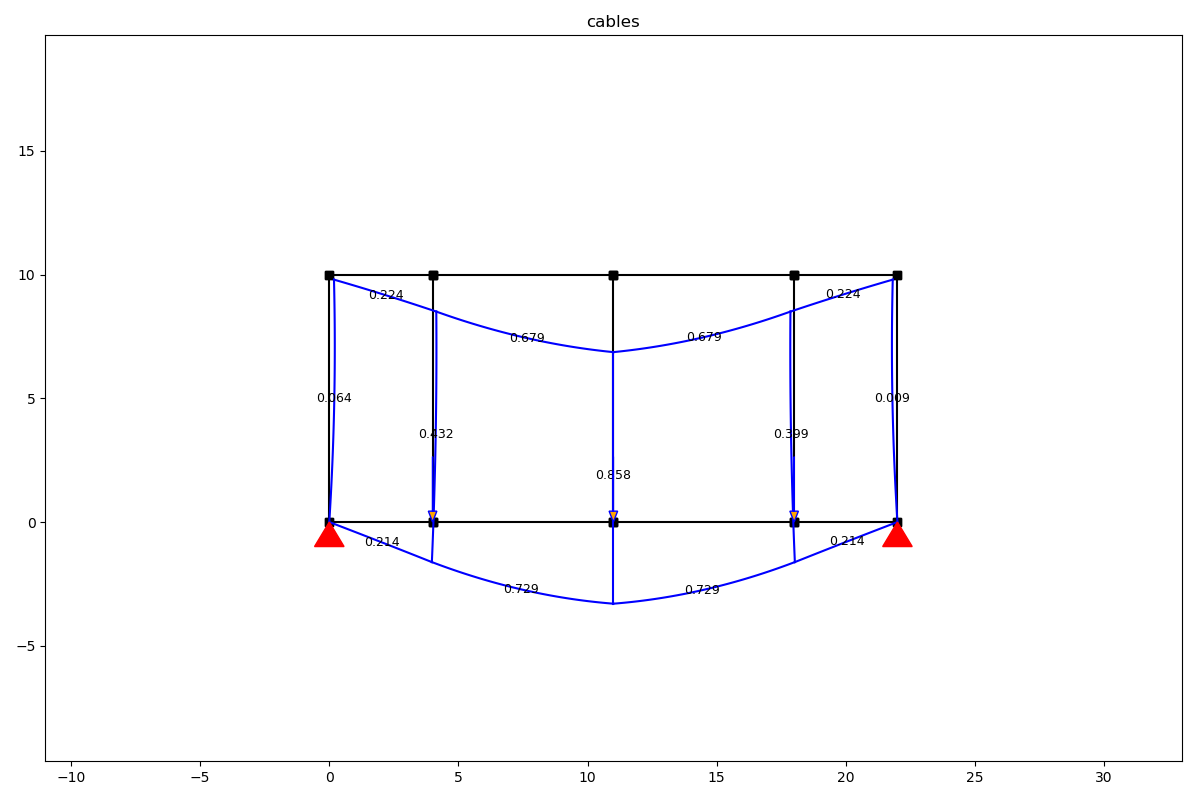
lc_cables = LoadCase('cables')
lc_cables.point_load(node_id=[2, 3, 4], Fy=-100)
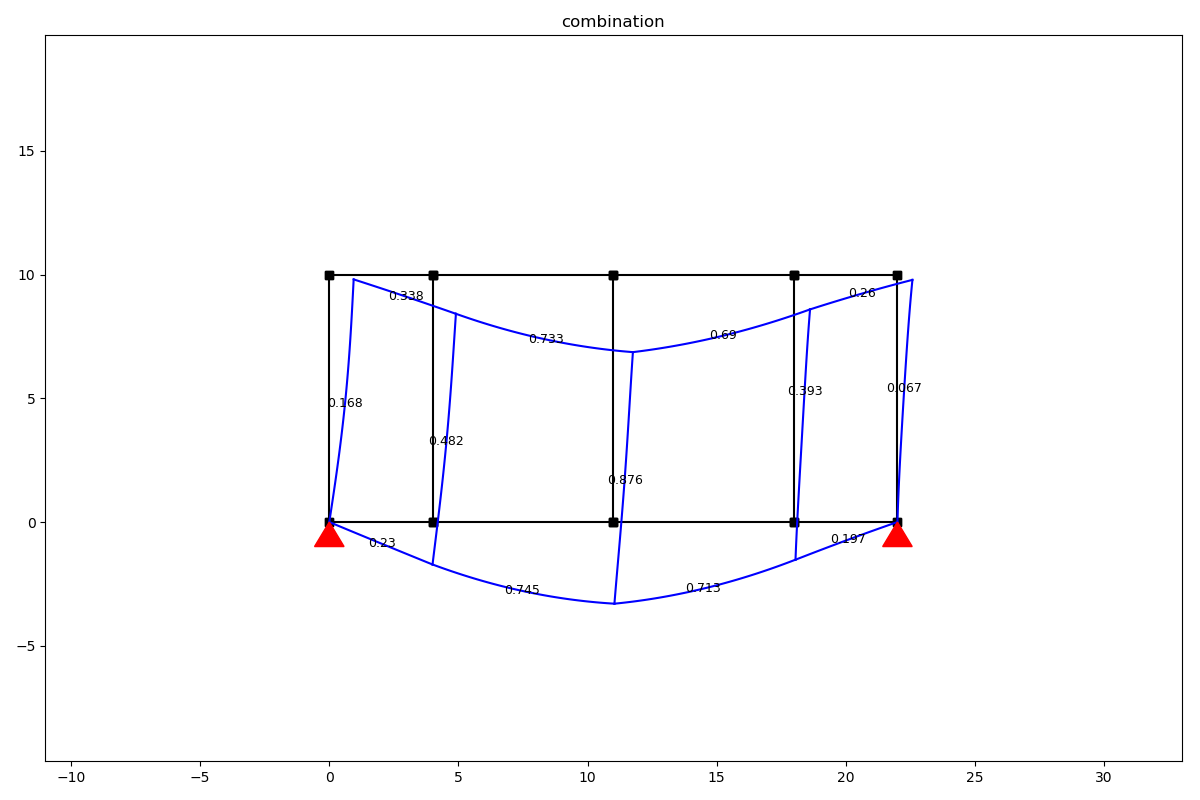
combination = LoadCombination('ULS')
combination.add_load_case(lc_wind, 1.5)
combination.add_load_case(lc_cables, factor=1.2)
Now we can make a separate calculation for every load case and for the whole load combination. We solve the combination by calling the solve method and passing our SystemElements model. The solve method returns a dictionary where the keys are the load cases and the values are the unique SystemElement objects for every load case. There is also a key combination in the results dictionary.
results = combination.solve(ss)
for k, ss in results.items():
results[k].show_structure()
results[k].show_displacement(show=False)
plt.title(k)
plt.show()
Load case wind
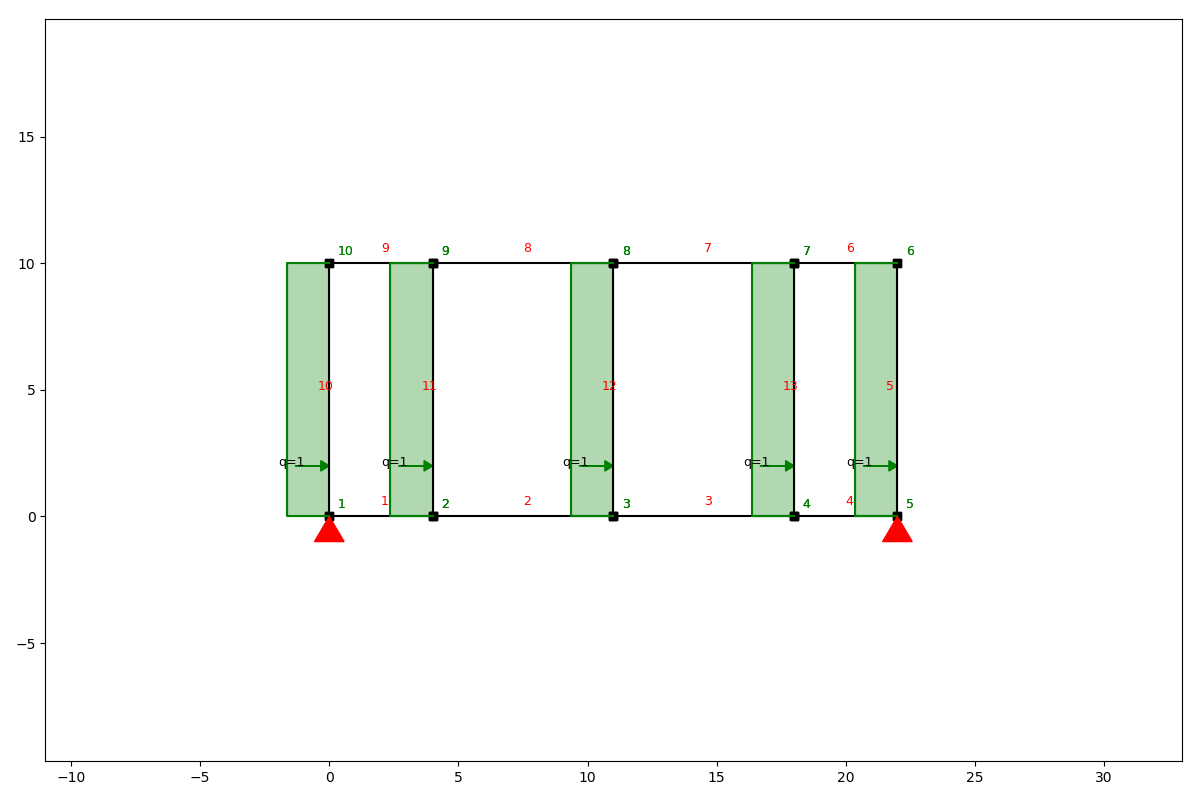
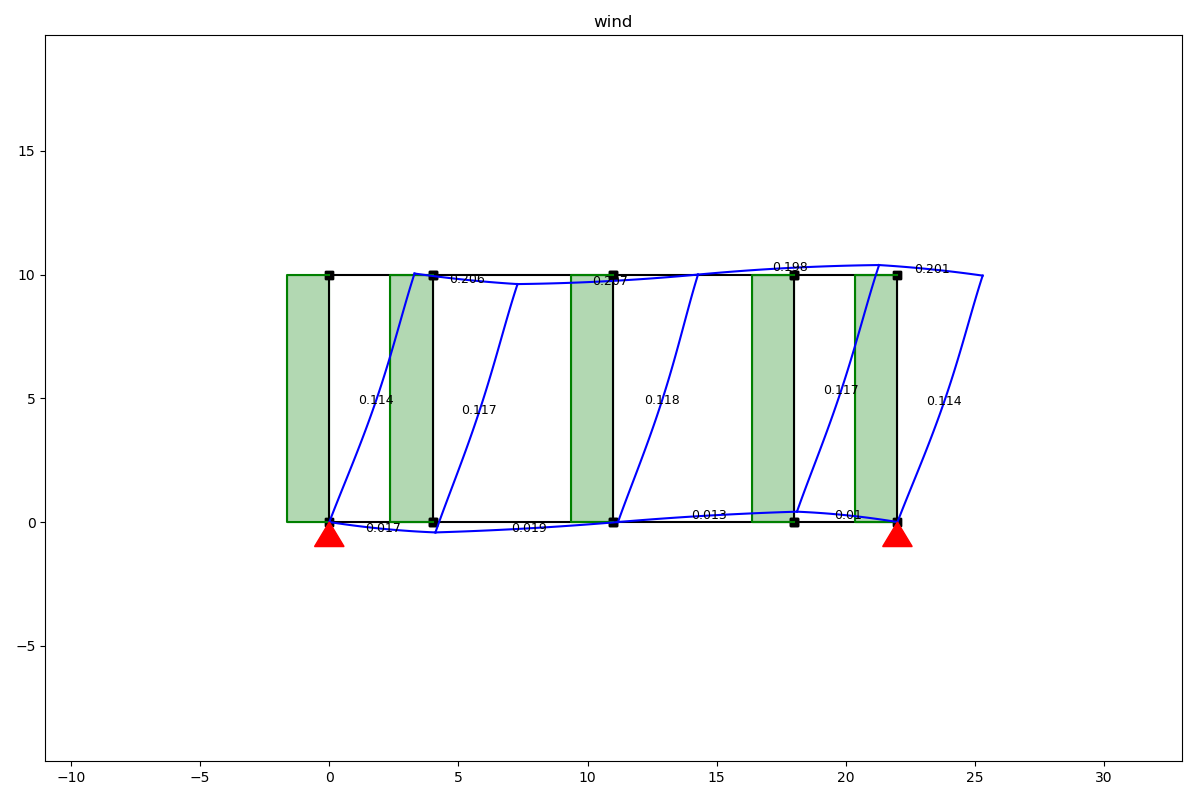
Load case cables
Combination
Load case class¶
-
class
anastruct.fem.util.load.LoadCase(name)[source]¶ Group different loads in a load case
-
dead_load(element_id, g)[source]¶ Apply a dead load in kN/m on elements.
Parameters: - element_id – (int/ list) representing the element ID
- g – (flt/ list) Weight per meter. [kN/m] / [N/m]
-
moment_load(node_id, Ty)[source]¶ Apply a moment on a node.
Parameters: - node_id – (int/ list) Nodes ID.
- Ty – (flt/ list) Moments acting on the node.
-
Load combination class¶
-
class
anastruct.fem.util.load.LoadCombination(name)[source]¶ -
-
add_load_case(lc, factor)[source]¶ Add a load case to the load combination.
Parameters: - lc – (
anastruct.fem.util.LoadCase) - factor – (flt) Multiply all the loads in this LoadCase with this factor.
- lc – (
-
solve(system, force_linear=False, verbosity=0, max_iter=200, geometrical_non_linear=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Evaluate the Load Combination.
Parameters: - system – (
anastruct.fem.system.SystemElements) Structure to apply loads on. - force_linear – (bool) Force a linear calculation. Even when the system has non linear nodes.
- verbosity – (int) 0: Log calculation outputs. 1: silence.
- max_iter – (int) Maximum allowed iterations.
- geometrical_non_linear – (bool) Calculate second order effects and determine the buckling factor.
Returns: (ResultObject)
- Development **kwargs:
param naked: (bool) Whether or not to run the solve function without doing post processing. param discretize_kwargs: When doing a geometric non linear analysis you can reduce or increase the number of elements created that are used for determining the buckling_factor
- system – (
-